
Deep Reinforcement Learning (CS-866)
Department of Computer Science
University of the Punjab
CartPole with REINFORCE (Policy Gradient)
Instructor: Nazar Khan
Goal¶
- We will train a neural network that outputs probabilities of actions that can be applied to a cart to balance a pole attached to it.
- The network becomes more likely to repeat actions that led to good outcomes.
Imports¶
In [2]:
# We import Gymnasium to create RL environments like CartPole
import gymnasium as gym
# Torch is the PyTorch library for building and training neural networks
import torch
# nn gives us building blocks for neural networks (layers, activations, etc.)
import torch.nn as nn
# optim gives us optimization algorithms like Adam to adjust network weights
import torch.optim as optim
# numpy is a numerical library (we'll use it a tiny bit)
import numpy as np
Define the Neural Network that will represent the policy¶
In [3]:
class PolicyNetwork(nn.Module):
# This class defines our neural network (our policy function π(a|s; θ))
# It takes in the state and outputs probabilities for each action.
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim):
# state_dim = number of numbers that describe the state (CartPole has 4)
# action_dim = number of possible actions (CartPole has 2: left or right)
super().__init__()
# nn.Sequential lets us stack layers in order, like a list
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(state_dim, 128), # first layer: input vector mapped to 128 neurons
nn.ReLU(), # activation function: adds non-linearity
nn.Linear(128, action_dim), # second layer: 128 neurons mapped to number of actions
nn.Softmax(dim=-1) # convert numbers into probabilities
)
def forward(self, x):
# forward defines how input flows through the network
return self.net(x)
Implementation of the REINFORCE algorithm for learning neural network parameters of optimal policy¶
In [4]:
def reinforce(env_name='CartPole-v1', gamma=0.99, lr=1e-3, episodes=500):
# Create the environment
env = gym.make(env_name)
# Get size of state and action spaces from environment
state_dim = env.observation_space.shape[0] # e.g., 4 for CartPole
action_dim = env.action_space.n # e.g., 2 actions
# Create the neural network policy
policy = PolicyNetwork(state_dim, action_dim)
# Adam optimizer will adjust neural network weights based on gradients
optimizer = optim.Adam(policy.parameters(), lr=lr)
# Keep track of total reward each episode to see learning progress
returns_history = []
# Loop over episodes of training
for episode in range(episodes):
# Reset environment at start of episode and get initial state
state, _ = env.reset()
# Lists to store log-probabilities and rewards for this episode
log_probs = []
rewards = []
done = False # episode is not finished yet
# Generate an episode
while not done:
# Convert state list/array to PyTorch tensor (NEEDED for network input)
state_tensor = torch.tensor(state, dtype=torch.float32)
# Forward pass: get action probabilities from policy network
action_probs = policy(state_tensor)
# Turn probabilities into a "distribution" (randomness)
dist = torch.distributions.Categorical(action_probs)
# Sample an action according to probabilities
action = dist.sample()
# Save log(probability(action_taken)) for learning update later
log_probs.append(dist.log_prob(action))
# Take action in environment and observe next state and reward
state, reward, done, truncated, _ = env.step(action.item())
# Save reward to compute return G later
rewards.append(reward)
# Episode finished. Now compute returns (discounted reward sums)
returns = []
G = 0 # return accumulator
# Compute returns G_t for each time step t, working backwards
for r in reversed(rewards):
G = r + gamma * G # Bellman return formula
returns.insert(0, G)
# Convert to PyTorch tensor so gradients flow properly
returns = torch.tensor(returns, dtype=torch.float32)
# Normalize returns. This helps stable training (optional but recommended)
returns = (returns - returns.mean()) / (returns.std() + 1e-9)
# Compute loss = −Σ log(pi(action|state)) * G_t
# (negative because we want gradient ASCENT, but optimizer does DESCENT)
loss = 0
for log_p, Gt in zip(log_probs, returns):
loss += -log_p * Gt
# Backpropagation step
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear old gradients
loss.backward() # compute gradients
optimizer.step() # update neural network weights
# Store total reward for this episode for plotting later
returns_history.append(sum(rewards))
# Print progress occasionally
if episode % 20 == 0:
print(f"Episode {episode:4d} | Return = {sum(rewards):.2f}")
env.close()
return policy, returns_history
Train the policy network¶
In [5]:
policy, history = reinforce()
Episode 0 | Return = 8.00 Episode 20 | Return = 12.00 Episode 40 | Return = 17.00 Episode 60 | Return = 51.00 Episode 80 | Return = 28.00 Episode 100 | Return = 29.00 Episode 120 | Return = 40.00 Episode 140 | Return = 66.00 Episode 160 | Return = 53.00 Episode 180 | Return = 87.00 Episode 200 | Return = 32.00 Episode 220 | Return = 152.00 Episode 240 | Return = 118.00 Episode 260 | Return = 85.00 Episode 280 | Return = 87.00 Episode 300 | Return = 262.00 Episode 320 | Return = 133.00 Episode 340 | Return = 341.00 Episode 360 | Return = 448.00 Episode 380 | Return = 193.00 Episode 400 | Return = 340.00 Episode 420 | Return = 346.00 Episode 440 | Return = 496.00 Episode 460 | Return = 183.00 Episode 480 | Return = 516.00
Plot the learning curve¶
In [6]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(history)
plt.xlabel("Episode")
plt.ylabel("Return")
plt.title("REINFORCE Learning Curve (CartPole)")
plt.show()
Run 5 episodes either until failure or until 500 steps (whichever comes earlier)¶
In [7]:
import imageio
import cv2
from IPython.display import Image
def record_episodes(num_episodes=5, filename="episodes.gif"):
env = gym.make("CartPole-v1", render_mode="rgb_array")
frames = []
for episode in range(num_episodes):
state, _ = env.reset()
done = False
step = 0
while not done:
step += 1
# Convert state to tensor
state_t = torch.tensor(state, dtype=torch.float32)
probs = policy(state_t)
action = torch.argmax(probs).item()
# Act
state, reward, terminated, truncated, _ = env.step(action)
done = terminated or truncated
# Get frame
frame = env.render()
## frame is in RGB format but OpenCV expects it in BGR format
#frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
# Draw step number on frame
frame = cv2.putText(
frame,
f"Episode: {episode+1}, Step: {step}",
(10, 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
1, (255, 0, 0), 2
)
#cv2.imshow("CartPole", frame)
#cv2.waitKey(5) # Adjust speed (ms)
frames.append(frame)
env.close()
imageio.mimsave(filename, frames, fps=100)
print(f"Saved {filename}")
#cv2.destroyAllWindows()
filename = "REINFORCE_cartpole_episodes.gif"
record_episodes(num_episodes=5, filename=filename)
Saved REINFORCE_cartpole_episodes.gif
In [15]:
#Image(filename)
GIFs¶
In [9]:
import imageio
import cv2
def record_trained_gif(policy, filename="trained_cartpole.gif", max_steps=500):
env = gym.make("CartPole-v1", render_mode="rgb_array")
state, _ = env.reset()
frames = []
step = 0
done = False
while not done and step < max_steps:
step += 1
# Select greedy action from policy
state_t = torch.tensor(state, dtype=torch.float32)
probs = policy(state_t)
action = torch.argmax(probs).item()
state, r, terminated, truncated, _ = env.step(action)
done = terminated or truncated
frame = env.render()
frame = cv2.putText(frame.copy(),
f"Step {step}", (10, 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (255,0,0), 2)
frames.append(frame)
env.close()
imageio.mimsave(filename, frames, fps=30)
print(f"Saved {filename}")
record_trained_gif(policy)
Saved trained_cartpole.gif
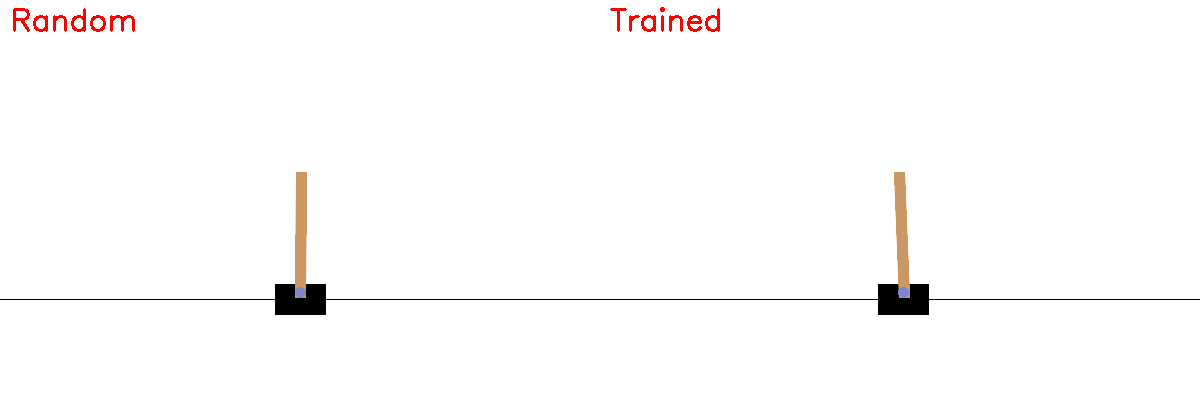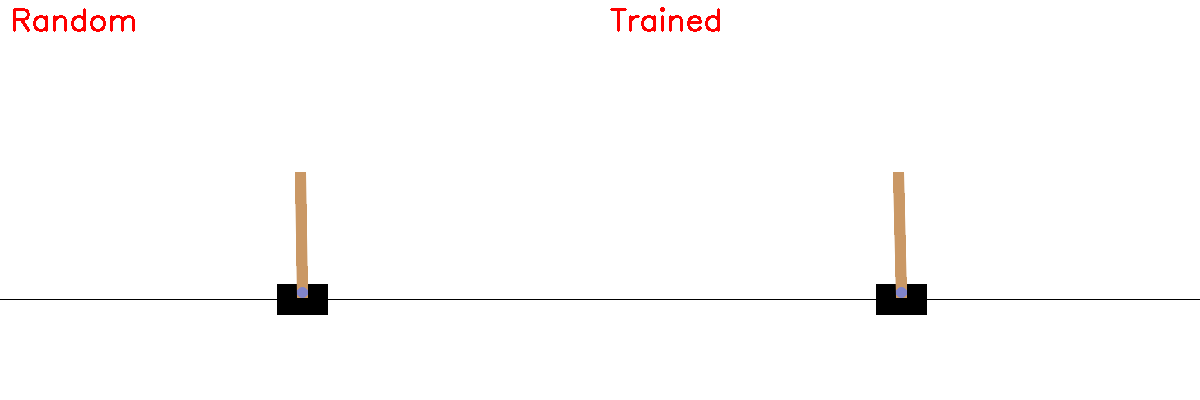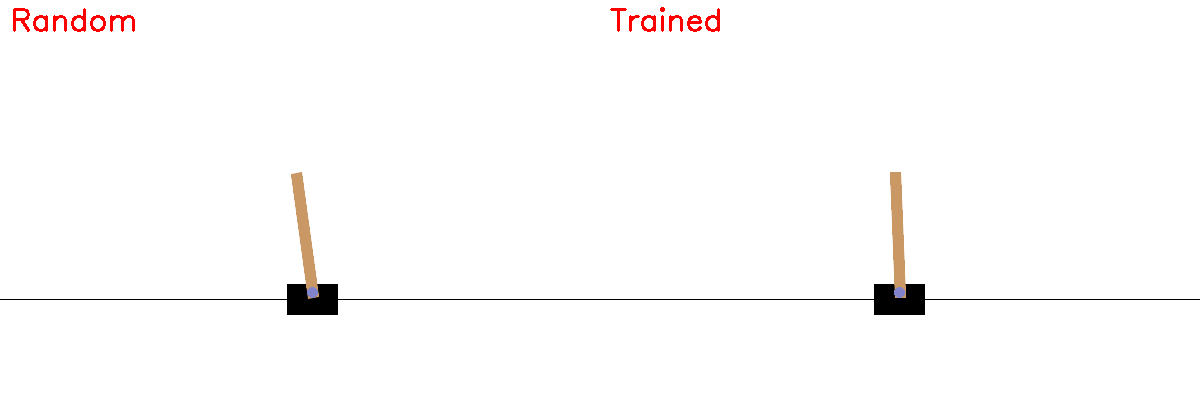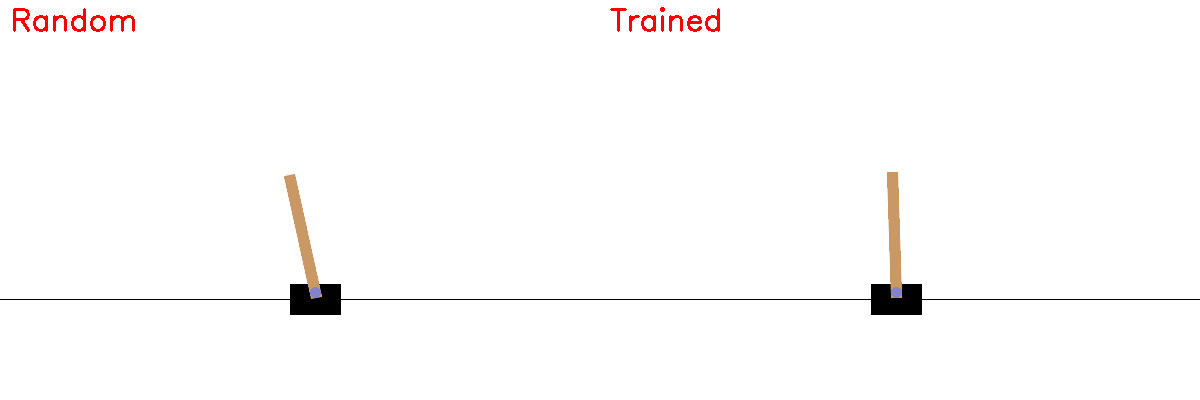
Random vs Trained Policy¶
In [14]:
from PIL import Image
def combine_frames(f1, f2):
return np.hstack([f1, f2])
def record_side_by_side(policy, filename="comparison.gif", max_steps=500):
env1 = gym.make("CartPole-v1", render_mode="rgb_array") # random
env2 = gym.make("CartPole-v1", render_mode="rgb_array") # trained
s1, _ = env1.reset()
s2, _ = env2.reset()
frames = []
for step in range(max_steps):
# --- Random Agent ---
a1 = env1.action_space.sample()
s1, _, d1, t1, _ = env1.step(a1)
frame_random = env1.render()
cv2.putText(frame_random, "Random", (10,30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (255,0,0), 2)
# --- Trained Agent ---
probs = policy(torch.tensor(s2, dtype=torch.float32))
a2 = torch.argmax(probs).item()
s2, _, d2, t2, _ = env2.step(a2)
frame_rl = env2.render()
cv2.putText(frame_rl, "Trained", (10,30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (255,0,0), 2)
frame = combine_frames(frame_random, frame_rl)
frames.append(frame)
if d1 or t1 or d2 or t2:
break
env1.close(); env2.close()
imageio.mimsave(filename, frames, fps=5)
print(f"Saved {filename}")
record_side_by_side(policy)
Saved comparison.gif
Live Policy Probability Plot¶
Shows how policy output evolves during one run (probs for LEFT vs RIGHT at every step)
In [11]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from IPython.display import clear_output, display
def run_with_live_probs(policy, episodes=1, max_steps=500):
env = gym.make("CartPole-v1", render_mode="rgb_array")
for ep in range(episodes):
state,_ = env.reset()
probs_list = []
for step in range(max_steps):
state_t = torch.tensor(state, dtype=torch.float32)
probs = policy(state_t).detach().numpy()
probs_list.append(probs)
action = np.argmax(probs)
state, _, terminated, truncated, _ = env.step(action)
# live plot
clear_output(wait=True)
plt.figure(figsize=(6,4))
arr = np.array(probs_list)
plt.plot(arr[:,0], label="LEFT")
plt.plot(arr[:,1], label="RIGHT")
plt.ylim(0,1)
plt.title(f"CartPole Policy Probabilities (Step {step})")
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
display(plt.gcf())
plt.close()
if terminated or truncated:
break
env.close()
run_with_live_probs(policy)
In [ ]: